An interesting circuit of a bicycle horn based on a popular, low cost telecom ringer chip is described here. This circuit can be powered using the bicycle dynamo supply and does not require batteries, which need to be replaced frequently. The section comprising diodes (D1 and D2) and capacitors (C1 and C2) forms a half-wave voltage-doubler circuit. The output of the voltage doubler is fed to capacitor C3 via resistor R1. The maximum DC supply that can be applied to the input terminals of IC1 is 28V. Therefore zener diode ZD1 is added to the circuit for protection and voltage regulation. The remainder of the circuit is the tone generator based on IC1 (KA2411).
Collection of electronics projects, circuit schematics design, diy hobby projects, printed circuit board softwares for students and hobbyists
Luxurious Toilet Bathroom Controller
Smart controller for your toilet and bathroom. The light and fan will automatic on when someone entere toilet or bathroom and off when no person inside it.
Aged persons in the house and guests often fumble while searching for the toilet and bathroom switches at night. Also, very few of us take care to switch off the lights of toilets/bathrooms after using them. The circuit given here helps to overcome both the problems. The figure shows two symmetrical circuits (one each for toilet and bathroom) sharing common power supply and a melody generator-cum-audio warning unit. The reed switches S1 and S2 are of normally-open type, operated by permanent magnets appropriately fixed to the doors of bathroom and toilet, respectively. When the doors of bathroom and toilet are closed, the reed switches are also closed, and vice versa. (Door is assumed in closed condition with nobody inside bathroom/toilet, i.e. reed switch is activated.)
Aged persons in the house and guests often fumble while searching for the toilet and bathroom switches at night. Also, very few of us take care to switch off the lights of toilets/bathrooms after using them. The circuit given here helps to overcome both the problems. The figure shows two symmetrical circuits (one each for toilet and bathroom) sharing common power supply and a melody generator-cum-audio warning unit. The reed switches S1 and S2 are of normally-open type, operated by permanent magnets appropriately fixed to the doors of bathroom and toilet, respectively. When the doors of bathroom and toilet are closed, the reed switches are also closed, and vice versa. (Door is assumed in closed condition with nobody inside bathroom/toilet, i.e. reed switch is activated.)
click for large image
Random Number Generator Game
This electronic game is simulation of one-arm bandit game. Electronics hobbyists will find it very interesting. When toggle switch S1 is in ‘run’ position, all segments of 7-segment displays (DIS1 through DIS3) will light up. On turning toggle switch S1 from ‘run’ to ‘stop’ position, displayed digits will continue advancing and the final display is unpredictable. Thus the final number displayed in DIS1 through DIS3 is of random nature. The speed with which the number in 7-segment display keeps changing on flipping switch S1 from ‘run’ to ‘stop’ condition slowly decays before stopping with a random number display. To play this game, one has to obtain three identical numbers in displays DIS1 through DIS3.
The contestant would score 1 (one) point if he manages to get a final display of ‘000’, 2 points for getting ‘111’ display, 3 points for ‘222’,… and so on—up to ten points for ‘999’. He should try to score maximum possible points in fixed numbers of attempts (say, 20 to 25 attempts). Apart from using this circuit as a game for entertainment, one can use it as random number generator for any other application as well. The decay time with the given component values is around 15 seconds before the display could stop at a final random number.
Circuit diagram:
The contestant would score 1 (one) point if he manages to get a final display of ‘000’, 2 points for getting ‘111’ display, 3 points for ‘222’,… and so on—up to ten points for ‘999’. He should try to score maximum possible points in fixed numbers of attempts (say, 20 to 25 attempts). Apart from using this circuit as a game for entertainment, one can use it as random number generator for any other application as well. The decay time with the given component values is around 15 seconds before the display could stop at a final random number.
Circuit diagram:
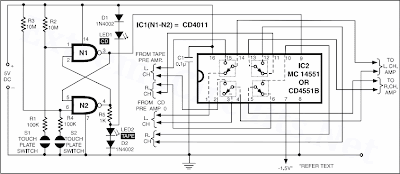
Audio Source Touch Selector
Often you need to connect output from more than one source (preamplifier) such as tape recorder/player and CD (compact disc) player to audio power amplifier. This needs disconnecting/connecting wires when you want to change the source, which is quite cumbersome and irritating. Here is a circuit that helps you choose between two stereo sources by simple touch of your hand. This circuit is so compact that it can be fixed within the audio power amplifier cabinet and can use the same power supply source. The circuit uses just two CMOS ICs and a few other componenets. The ICs used are MC14551/CD4551 (quad 2-channel analogue multiplexer) and CD4011 (quad 2-input NAND gate).
Schematic:
click for large image
Musical Touch Bell UM66
This musical call bell circuit can be operated by just bridging the gap between the touchplates with one’s fingertips. Thus there is no need for a mechanical ‘on’/‘off’ switch because the touch-plates act as a switch. Other features include low cost and low power consumption. The bell can work on 1.5V or 3V, using one or two pencil cells, and can be used in homes and offices. Two transistors are used for sensing the finger touch and switching on a melody IC. Transistor BC148 is npn type while transistor BC558 is pnp type. The emitter of transistor BC148 is shorted to the ground, while that of transistor BC558 is connected to the positive terminal.
 |
| click for large image |
| Musical Touch Bell UM66 |
High / Low Voltage Cutoff With Timer
This inexpensive high / low voltage cutoff circuit can be connected to an air-conditioner/fridge or to any other sophisticated electrical appliance for its protection. Generally, costly voltage stabilizers are used with such appliances for maintaining constant AC voltage. However, due to fluctuations in AC mains supply, a regular ‘click’ sound in the relays is heard. The frequent energisation/de-energisation of the relays leads to electrical noise and shortening of the life of electrical appliances and the relay/stabilizer itself. The costly yet fault-prone stabiliser may be replaced by this inexpensive high-low cutout circuit with timer.
The circuit is so designed that relay RL1 gets energised when the mains voltage is above 270V. This causes resistor R8 to be inserted in series with the load and thereby dropping most of the voltage across it and limiting the current through the appliance to a very low value. If the input AC mains is less than 180 volts or so, the low-voltage cut-off circuit interrupts the supply to the electrical appliance due to energisation of relay RL2. After a preset time delay of one minute (adjustable), it automatically tries again. If the input AC mains supply is still low, the power to the appliance is again interrupted for another one minute, and so on, until the mains supply comes within limits (>180V AC).
Circuit diagram:
The circuit is so designed that relay RL1 gets energised when the mains voltage is above 270V. This causes resistor R8 to be inserted in series with the load and thereby dropping most of the voltage across it and limiting the current through the appliance to a very low value. If the input AC mains is less than 180 volts or so, the low-voltage cut-off circuit interrupts the supply to the electrical appliance due to energisation of relay RL2. After a preset time delay of one minute (adjustable), it automatically tries again. If the input AC mains supply is still low, the power to the appliance is again interrupted for another one minute, and so on, until the mains supply comes within limits (>180V AC).
Circuit diagram:
 |
| High / Low Voltage Cutoff With Timer Schematic |
Automatic Heat Detector
This Automatic Heat Detector circuit uses a complementary pair comprising npn metallic transistor T1 (BC109) and pnp germanium transistor T2 (AC188) to detect heat (due to outbreak of fire, etc) in the vicinity and energise a siren. The collector of transistor T1 is connected to the base of transistor T2, while the collector of transistor T2 is connected to relay RL1. The second part of the circuit comprises popular IC UM3561 (a siren and machine-gun sound generator IC), which can produce the sound of a fire-brigade siren. Pin numbers 5 and 6 of the IC are connected to the +3V supply when the relay is in energized state, whereas pin 2 is grounded.
Circuit diagram:
Circuit diagram:
 |
| Automatic Heat Detector Circuit |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)